SELinux
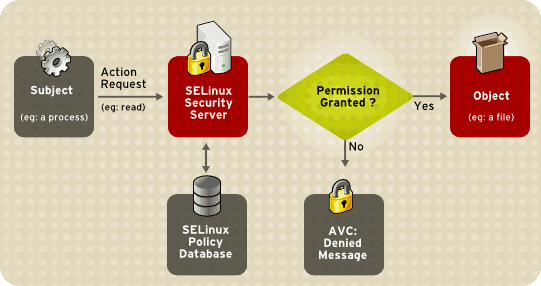
The diagram below shows the process a process requesting access to a file goes through before it is granted access using SELinux:
Reference:
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/5/html/Deployment_Guide/images/SELinux_Decision_Process.png
SELinux Modes:
1) Enforcing - AVC is checked, logged and enforced
2) Permissive - AVC is checked and logged however rules are NOT enforced
3) Disabled
Managing SELinux
1) SELinux Tools
2) /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Resolving Label Issue
If SELinux has been disabled for a while, chances are the labels for some directories and files will be incorrect. To reset the system to the correct labels you will need to create the following file and then reboot the system:
/.autorelabelWhen the system reboots then this file will cause the relabel to happen early in the boot process.
SE Policie Control
SELINUXTYPE=targeted|strict
E.g.
You are able to target the following daemons: dhcpd, httpd (apache.te), named, nscd, ntpd, portmap, snmpd, squid
SELINUXTYPE=httpd|strict
You are able to control policy enforcement for daemons using boolean values:
Value 1 - disabled SELinux protection for a daemon.
List SELinux Booleans
| SEBool Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Enabled |
| 1 | Disabled |
The following command lists all SELinux booleans
getsebool -aThe following command is slightly better, you can view default preferences. EG. will is start on boot
semanage boolean -l | grep httpdThe following command